hi
Challenge Description: Identify hidden function and access it using gdb Challenge File: o.exe
Run file command on the binary and execute binary to understand its behaviour
$ file o.exe
o.exe: ELF 64-bit LSB pie executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=50ac482d6d4b0e7681add7a7374a7740524cef28, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
$ ./o.exe
Enter your name: test
Hi test
Based on our initial analysis, this is 64 bit ELF binary that takes in string input and print out with Hi <input>.
Identify hidden function in decompiler
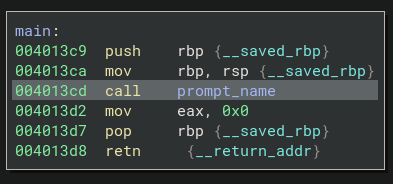
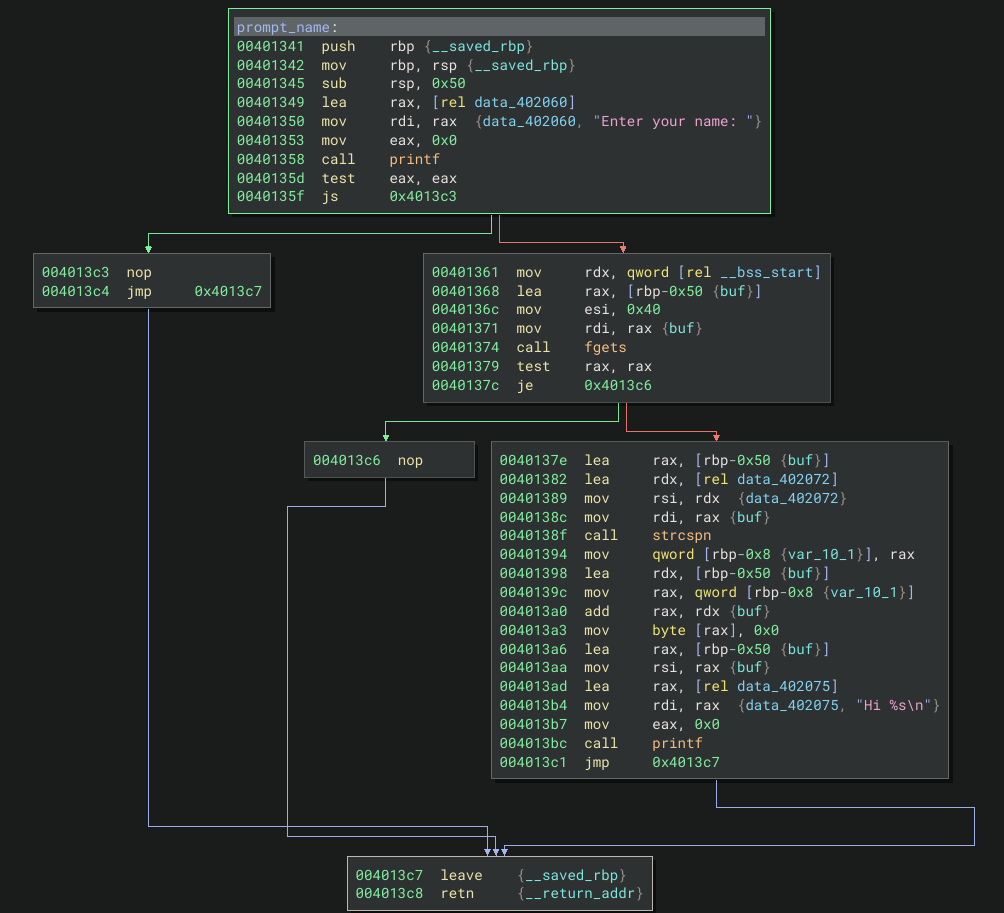
From the main function, it calls function prompt_name and prints out Enter your name: and use fgets to get input string, stores the reference address in RDI register and using printf to print it out.
However from the symbol tree, there are three functions at lower address function that not been called.
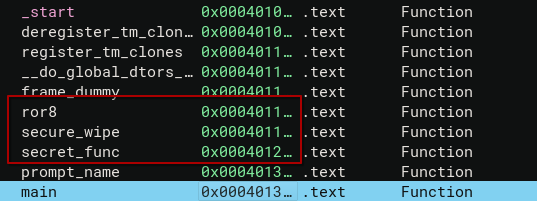
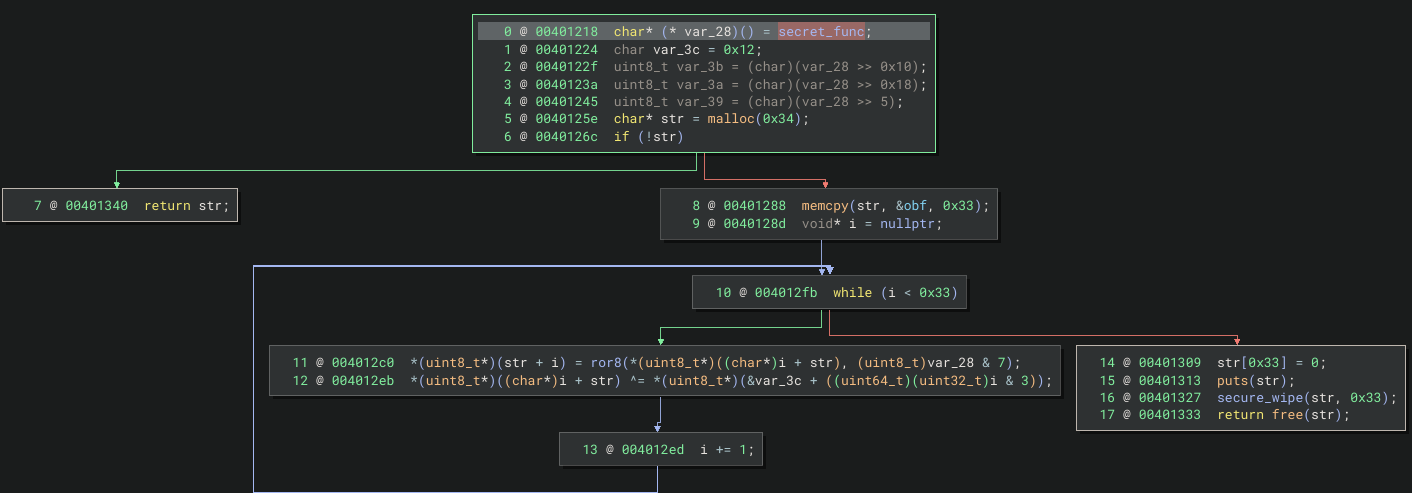
Here is how secret_func() works:
- reads its own function address and extract bytes at offset of
0x5, 0x10, 0x18 - using malloc to allocate the encrypted flag from obf
- perform ROR & 7
- XOR with rotated by with four local bytes
Here is the simplified form
str[i] = ROR8(str[i], rot) ^ key[i & 3]
Because the rotation amount depends on the function pointer, and the XOR key depends on specific bytes extracted from that same pointer or address, the decryption outputs relies on how the binary is loaded with dynamic addressing. So next task is to use gdb debugger to get runtime address of secret_func and extract the obfuscated bytes of obf.
Using gdb to find runtime function address of secret_func
pwndbg> p secret_func
$2 = {<text variable, no debug info>} 0x555555555208 <secret_func>
pwndbg>
With that using a script to get the flag, here is the script:
def ror8(value, shift):
"""rotate right 8-bit value"""
shift = shift & 7
return ((value >> shift) | (value << (8 - shift))) & 0xff
def decrypt_obf(obf_bytes, func_addr):
"""
decrypt the obf data using the secret_func address
args:
obf_bytes: bytes object containing encrypted data
func_addr: address of secret_func (e.g., 0x1208)
"""
# generate key from function address (same as original code)
# note: shifts are on the full value, then masked to byte
key = [
(func_addr >> 8) & 0xff, # v1[0] - bits 8-15
(func_addr >> 16) & 0xff, # v1[1] - bits 16-23
(func_addr >> 24) & 0xff, # v1[2] - bits 24-31
(func_addr >> 5) & 0xff # v1[3] - bits 5-12
]
rotation = func_addr & 7 # v3 - bits 0-2
decrypted = bytearray()
# apply decryption to each byte
for i, byte in enumerate(obf_bytes):
# rotate right
rotated = ror8(byte, rotation)
# xor with key
decrypted.append(rotated ^ key[i & 3])
return bytes(decrypted)
# actual data from the binary
if __name__ == "__main__":
# runtime address of secret_func (from pwndbg)
func_addr = 0x555555555208
# obf bytes from 0x00402020
obf_bytes = bytes([
0x10, 0x1a, 0x1d, 0xa2, 0x67, 0x2e, 0x11, 0xa1,
0x36, 0x0a, 0x20, 0xcf, 0x21, 0x65, 0x39, 0xe6,
0x61, 0x31, 0x0a, 0xf9, 0x26, 0x0a, 0x22, 0xa1,
0x65, 0x3d, 0x65, 0xe5, 0x65, 0x0a, 0x16, 0xd8,
0x33, 0x62, 0x12, 0xc0, 0x65, 0x0a, 0x6a, 0xcf,
0x05, 0x66, 0x64, 0xa1, 0x0d, 0x11, 0x65, 0xfe,
0x61, 0x74, 0x28
])
# verify with known plaintext
known_plain = b"boh25{"
print(f"known plaintext start: {known_plain}")
print(f"encrypted start: {obf_bytes[:6].hex()}")
# work backwards to find key
print("\nreverse engineering key from known plaintext:")
derived_key = []
for i in range(6):
# since rotation is 0 for addr 0x1208, encrypted = plain xor key[i&3]
xor_val = obf_bytes[i] ^ known_plain[i]
derived_key.append(xor_val)
print(f" byte {i}: 0x{obf_bytes[i]:02x} xor 0x{known_plain[i]:02x} = 0x{xor_val:02x}")
print(f"\nderived key pattern: {[f'0x{k:02x}' for k in derived_key[:4]]}")
print()
print(f"function address: 0x{func_addr:x}")
print(f"calculated key: {[f'0x{k:02x}' for k in [
(func_addr >> 8) & 0xff,
(func_addr >> 16) & 0xff,
(func_addr >> 24) & 0xff,
(func_addr >> 5) & 0xff
]]}")
print(f"rotation: {func_addr & 7}")
print()
print(f"encrypted obf ({len(obf_bytes)} bytes):")
print(" ".join(f"{b:02x}" for b in obf_bytes))
print()
result = decrypt_obf(obf_bytes, func_addr)
print(f"decrypted ({len(result)} bytes):")
print("hex:", result.hex())
print()
try:
decoded = result.decode('ascii')
print("decrypted string:")
print(decoded)
except unicodedecodeerror:
print("could not decode as ascii, raw bytes:")
print(result)
Flag: BOH25{D1d_u_s0lv3d_it_w17h0u7_CHa7GP7_?_W311_D0n3!}