New Hire
After the intern left and was arrested for hacking his previous company, the company has finally decided to take in new hires! What could go wrong? Oh no, the company was hacked again! We have gathered evidence from the attacker’s machine!
- Category: Forensic
- Challenge File: kali.zip
Solutions:
1. Extract the archieved file and view its contents
$ unzip kali.zip
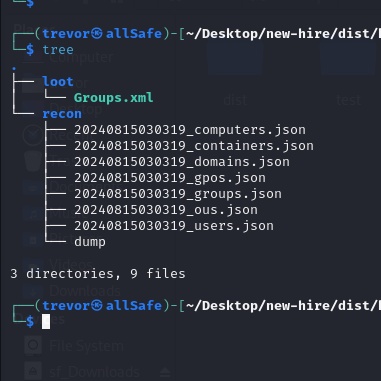
Neglect the dump file is not part of the challenge file, is from my output
2. View Groups.xml from loot directory
$ xmllint --format Groups.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Groups clsid="{3125E937-EB16-4b4c-9934-544FC6D24D26}">
<User clsid="{DF5F1855-51E5-4d24-8B1A-D9BDE98BA1D1}" name="rgraham" image="2" changed="2024-08-15 06:59:13" uid="{BDA116FC-0E8C-4784-887F-71C9573859E3}">
<Properties action="U" newName="" fullName="" description="" cpassword="FKhE/Beywcp8ZLLxH6LszmcuRiXceWaeEXvSJ5jKyJjqJ9vAidZiHVebDcE6n+Wi" changeLogon="0" noChange="0" neverExpires="0" acctDisabled="0" userName="rgraham"/>
</User>
</Groups>
From this XML file, we can know this is a Group Policy configuration file which contain user settings. These details can be summarized:
- Username: rgraham
- Last changed: August 15, 2024
- Contains an encrypted password (cpassword field)
- Account status: Active (not disabled)
- Password settings: Can be changed (no restrictions) and can expire
This is a Group Policy Preferences (GPP) XML file that is use for Active Directory to manage user account. However, since the password in cpassword file in encrypted, it is exploitable and able to decrypt with the tool of gpp-decrypt
- Information about GPP Vulnerability: article
3. Decrypt GPP cpassword
$ gpp-decrypt FKhE/Beywcp8ZLLxH6LszmcuRiXceWaeEXvSJ5jKyJjqJ9vAidZiHVebDcE6n+Wi
L1ke_OscP_@gAiN}
Here we got the second part of the flag, the first part should be in the json file from recon directory
4. Find the first part the flag
Before start searching for the first part like a barbarian, we have to know the pattern of how the json file is categorized. We notice computers, containers,domains, gpos, groups, ous, users. Based on it, we can it is from BloodHound active directory whereby attacker collected credentials information with BloodHound and it generates JSON file.
- Information of BloodHound JSON Object Formats: bloodhound.readthedocs.io
For the first part of the flag, it is locate at 20240815030319_users.json file
jq . 20240815030319_users.json | grep description
We will notice a base64 encoded string
VwBlACAAZABpAGQAbgAnAHQAIABsAGUAYQByAG4AIABvAHUAcgAgAGwAZQBzAHMAbwBuACAAcwBvACAAdABoAGkAcwAgAGkAcwAgAG8AbgBlACAAaABhAGwAZgAgAG8AZgAgAHQAaABlACAAZgBsAGEAZwA6ACAASQBCAE8ASAAyADQAewBBAEQAXwBQAFcATgAzAGQAXwA=
5. Decode the base64 string
$ echo "VwBlACAAZABpAGQAbgAnAHQAIABsAGUAYQByAG4AIABvAHUAcgAgAGwAZQBzAHMAbwBuACAAcwBvACAAdABoAGkAcwAgAGkAcwAgAG8AbgBlACAAaABhAGwAZgAgAG8AZgAgAHQAaABlACAAZgBsAGEAZwA6ACAASQBCAE8ASAAyADQAewBBAEQAXwBQAFcATgAzAGQAXwA=" | base64 -d
We didn't learn our lesson so this is one half of the flag: IBOH24{AD_PWN3d_
So we got the first part and second part of the flag
Flag: IBOH24{AD_PWN3d_L1ke_OscP_@gAiN}