Challenge 1
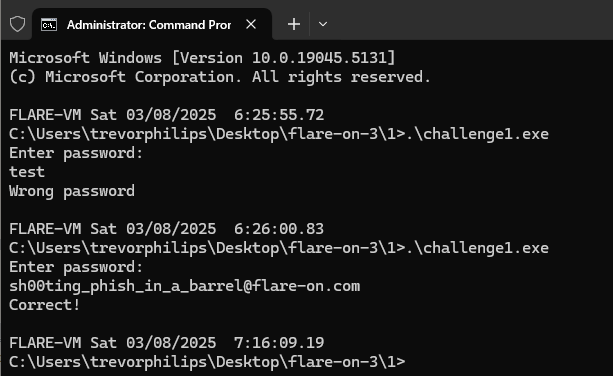
Using command prompt to run the challenge executable will prompt to enter password.
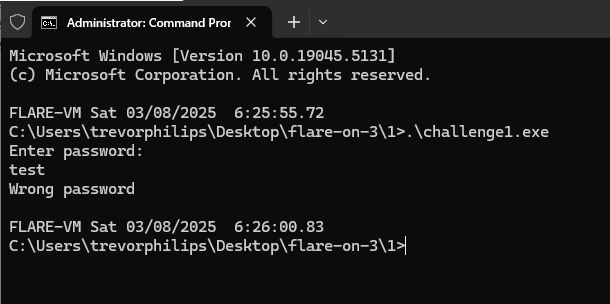
Solution:
1. Use IDA to disassemble to challenge executable
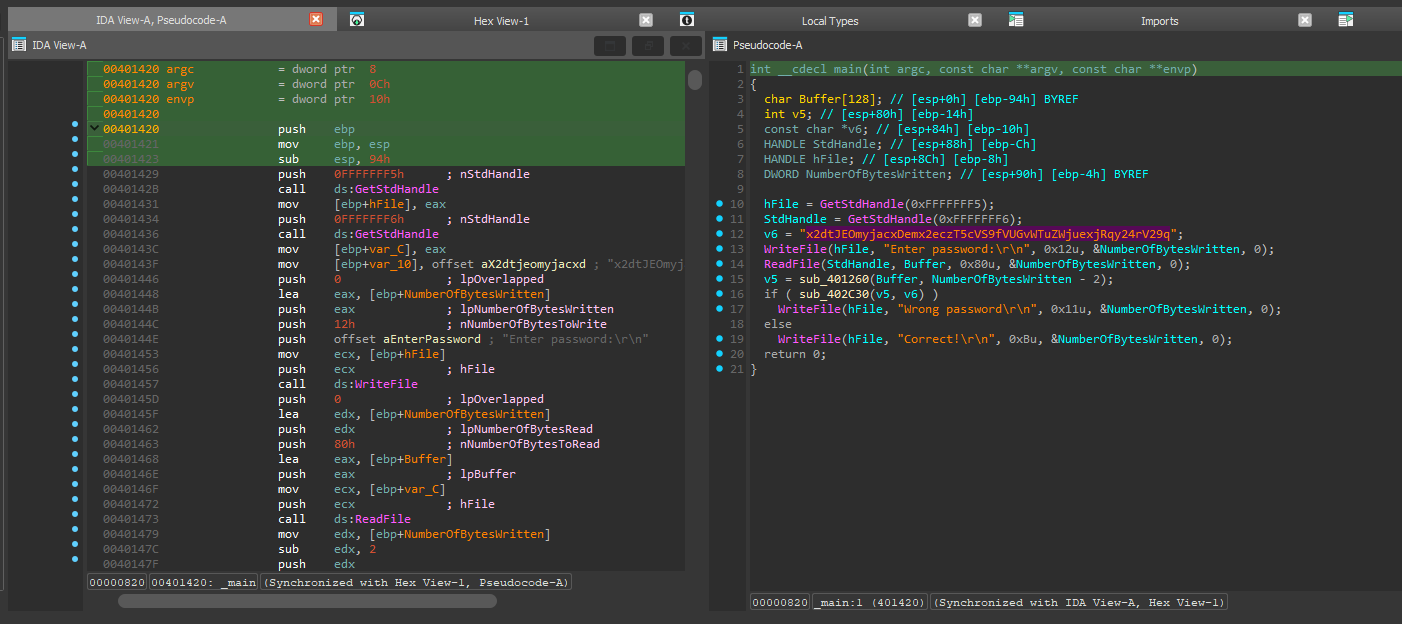
Here the main function use Windows API function (WriteFile, ReadFile) to display text and takes user input.
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
char Buffer[128]; // [esp+0h] [ebp-94h] BYREF
int v5; // [esp+80h] [ebp-14h]
const char *v6; // [esp+84h] [ebp-10h]
HANDLE StdHandle; // [esp+88h] [ebp-Ch]
HANDLE hFile; // [esp+8Ch] [ebp-8h]
DWORD NumberOfBytesWritten; // [esp+90h] [ebp-4h] BYREF
hFile = GetStdHandle(0xFFFFFFF5);
StdHandle = GetStdHandle(0xFFFFFFF6);
v6 = "x2dtJEOmyjacxDemx2eczT5cVS9fVUGvWTuZWjuexjRqy24rV29q";
WriteFile(hFile, "Enter password:\r\n", 0x12u, &NumberOfBytesWritten, 0);
ReadFile(StdHandle, Buffer, 0x80u, &NumberOfBytesWritten, 0);
v5 = sub_401260(Buffer, NumberOfBytesWritten - 2);
if ( sub_402C30(v5, v6) )
WriteFile(hFile, "Wrong password\r\n", 0x11u, &NumberOfBytesWritten, 0);
else
WriteFile(hFile, "Correct!\r\n", 0xBu, &NumberOfBytesWritten, 0);
return 0;
}
User input is stored in Buffer and then will be use as argument for sub_401260, which then uses v5 to stored as it result. The function sub402C30 is a strcmp function which compares the value of v5 and v6. Our next objective is to reverse the function sub_401260.
2. Reverse the function of sub_401260
Here is the decompile function of sub_401260:
int __cdecl sub_401260(int a1, unsigned int a2)
{
int v3; // [esp+Ch] [ebp-24h]
int v4; // [esp+10h] [ebp-20h]
int v5; // [esp+14h] [ebp-1Ch]
int i; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-14h]
unsigned int v7; // [esp+20h] [ebp-10h]
int v8; // [esp+24h] [ebp-Ch]
int v9; // [esp+28h] [ebp-8h]
int v10; // [esp+28h] [ebp-8h]
unsigned int v11; // [esp+2Ch] [ebp-4h]
v8 = sub_402CBC(4 * ((a2 + 2) / 3) + 1);
if ( !v8 )
return 0;
v11 = 0;
v9 = 0;
while ( v11 < a2 )
{
v5 = *(unsigned __int8 *)(v11 + a1);
if ( ++v11 >= a2 )
{
v4 = 0;
}
else
{
v4 = *(unsigned __int8 *)(v11 + a1);
++v11;
}
if ( v11 >= a2 )
{
v3 = 0;
}
else
{
v3 = *(unsigned __int8 *)(v11 + a1);
++v11;
}
v7 = v3 + (v5 << 16) + (v4 << 8);
*(_BYTE *)(v9 + v8) = byte_413000[(v7 >> 18) & 0x3F];
v10 = v9 + 1;
*(_BYTE *)(v10 + v8) = byte_413000[(v7 >> 12) & 0x3F];
*(_BYTE *)(++v10 + v8) = byte_413000[(v7 >> 6) & 0x3F];
*(_BYTE *)(++v10 + v8) = byte_413000[v3 & 0x3F];
v9 = v10 + 1;
}
for ( i = 0; i < dword_413040[a2 % 3]; ++i )
*(_BYTE *)(v8 + 4 * ((a2 + 2) / 3) - i - 1) = 61;
*(_BYTE *)(4 * ((a2 + 2) / 3) + v8) = 0;
return v8;
}
Examining the operation of the function, it process in a 3-byte chunks, using shift left (<<) and right (>>) operations to manipulate the data.
- Memory Allocation: The function first allocates memory using
sub_402CBC. The required buffer size is calculated as4 * ((a2 + 2) / 3) + 1, which ensures enough space for the Base64-encoded output, including the null terminator. - Processing in 3-Byte Chunks: It iterates through
a1, reading three bytes at a time. If there are fewer than three bytes remaining, the missing bytes are set to zero. - Bit Manipulation: Each 3-byte sequence is converted into a single 24-bit integer (
v7 = v3 + (v5 << 16) + (v4 << 8)). The function then extracts four 6-bit segments by shifting and masking. - Base64 Encoding: These 6-bit segments serve as indices into
byte_413000which is the Base64 lookup table. The corresponding Base64 characters are stored in the output buffer. - Padding Handling: If the input size (
a2) is not a multiple of 3, the function appends padding characters (=) as determined bydword_413040[a2 %3]. - Finalizing Output: The encoded string is null-terminated before being returned.
However, the lookup table for the Base64 string is modified, we can notice the byte_413040 starts with Z as beginning. We can take a look in the memory dump of x32dbg:
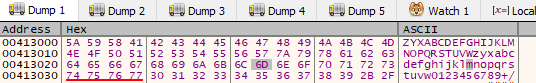
If using the Find References tools from x32dbg is shows using is used as the lookup table to map and encoded as the output.
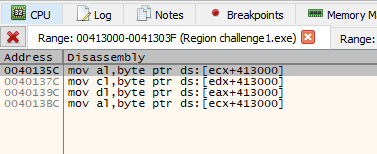
According to this resource, it shows the Base64 index mapping table starts with like this ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/. For our case is ZYXABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWzyxabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvw0123456789+/. So in order to reverse the “modified” Base64 encoded string from v6, we need a customized our solution script.
3. Decoding Base64 string with custom lookup table
Before proceeding to solution script, we have knew that v6 is the Base64 string which uses the custom lookup table, later is compared with the user input. Here is the Go reverse solution script:
package main
import (
"encoding/base64"
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
// Define the custom and standard Base64 alphabets
customB64 := "ZYXABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWzyxabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvw0123456789+/"
standardB64 := "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/"
// Encoded string
encodedStr := "x2dtJEOmyjacxDemx2eczT5cVS9fVUGvWTuZWjuexjRqy24rV29q"
// Translate the encoded string to standard Base64
translatedStr := translateCustomBase64(encodedStr, customB64, standardB64)
// Decode the translated string
decodedBytes, err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(translatedStr)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error decoding Base64:", err)
return
}
// Convert bytes to string
decodedStr := string(decodedBytes)
fmt.Println("Decoded string:", decodedStr)
}
// translateCustomBase64 translates a custom Base64 string to standard Base64
func translateCustomBase64(encodedStr, customB64, standardB64 string) string {
// Create a mapping from custom to standard Base64
translationMap := make(map[rune]rune)
for i, char := range customB64 {
translationMap[char] = rune(standardB64[i])
}
// Translate the encoded string
var translatedStr strings.Builder
for _, char := range encodedStr {
if standardChar, ok := translationMap[char]; ok {
translatedStr.WriteRune(standardChar)
} else {
translatedStr.WriteRune(char) // Handle padding characters (e.g., '=')
}
}
return translatedStr.String()
}
The output: sh00ting_phish_in_a_barrel@flare-on.com.
Flag: sh00ting_phish_in_a_barrel@flare-on.com